![]()
![]()
![]() -----------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------![]()
![]()
![]() THE EXISTENCE OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
THE EXISTENCE OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES ![]()
![]() In ancient times a well-known theory by the name of ‘Theory of Atomism’
was widely accepted. This theory was originally proposed by the
Greeks, in
particular by a man called Democritus, who lived about 23 centuries
ago.
Democritus and the people that came after him, assumed that the smallest unit
of matter was the atom. The Arabs used to believe the same. The
Arabic word
dharrah most commonly meant an atom. In recent times modern science has
discovered that it is possible to split even an atom. That the atom can be split
further is a development of the 20th century. Fourteen centuries ago this
concept would have appeared unusual even to an Arab. For him the dharrah
was the limit beyond which one could not go. The following Qur’aanic verse
however, refuses to acknowledge this limit:
In ancient times a well-known theory by the name of ‘Theory of Atomism’
was widely accepted. This theory was originally proposed by the
Greeks, in
particular by a man called Democritus, who lived about 23 centuries
ago.
Democritus and the people that came after him, assumed that the smallest unit
of matter was the atom. The Arabs used to believe the same. The
Arabic word
dharrah most commonly meant an atom. In recent times modern science has
discovered that it is possible to split even an atom. That the atom can be split
further is a development of the 20th century. Fourteen centuries ago this
concept would have appeared unusual even to an Arab. For him the dharrah
was the limit beyond which one could not go. The following Qur’aanic verse
however, refuses to acknowledge this limit:
![]() “The Unbelievers say, ‘Never to
us will come The Hour’: say, ‘Nay! But most surely, By my Lord, it will
come Upon you – by Him Who knows the unseen – From Whom is not
hidden The least little atom In the Heavens or on earth: Nor is there
anything less Than that, or greater, but Is in the Record Perspicuous.’”
[Al-Qur’aan 34:3]
“The Unbelievers say, ‘Never to
us will come The Hour’: say, ‘Nay! But most surely, By my Lord, it will
come Upon you – by Him Who knows the unseen – From Whom is not
hidden The least little atom In the Heavens or on earth: Nor is there
anything less Than that, or greater, but Is in the Record Perspicuous.’”
[Al-Qur’aan 34:3] ![]()
(A similar message is conveyed in the Qur’an in 10:61.)
![]() This verse refers to the Omniscience of God, His knowledge of all things,
hidden or apparent. It then goes further and says that God is aware of
everything, including what is smaller or bigger than the atom. Thus the verse
clearly shows that it is possible for something smaller than the atom to exist,
a
fact discovered only recently by modern science.
This verse refers to the Omniscience of God, His knowledge of all things,
hidden or apparent. It then goes further and says that God is aware of
everything, including what is smaller or bigger than the atom. Thus the verse
clearly shows that it is possible for something smaller than the atom to exist,
a
fact discovered only recently by modern science. ![]()
![]()
![]() -----------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------![]()
![]()
![]() THE WATER CYCLE
THE WATER CYCLE ![]()

![]() In 1580, Bernard Palissy was the first man to describe the present day concept
of ‘water cycle’. He described how water evaporates from the oceans and
cools to form clouds. The clouds move inland where they rise, condense and
fall as rain. This water gathers as lakes and streams and flows back to the
ocean in a continuous cycle. In the 7th century B.C., Thales of Miletus
believed that surface spray of the oceans was picked up by the wind and
carried inland to fall as rain. In earlier times people did not know the source
of underground water. They thought the water of the oceans, under the effect
of winds, was thrust towards the interior of the continents. They also believed
that the water returned by a secret passage, or the Great
Abyss. This passage
is connected to the oceans and has been called the ‘Tartarus’, since
Plato’s time. Even Descartes, a great thinker of the
eighteenth century, subscribed to
this view. Till the nineteenth century, Aristotle’s theory was prevalent.
According to this theory, water was condensed in cool mountain caverns and
formed underground lakes that fed springs. Today, we know that the
rainwater that seeps into the cracks of the ground is responsible for this.
The water cycle is described by the Qur’aan in the following
verses:
In 1580, Bernard Palissy was the first man to describe the present day concept
of ‘water cycle’. He described how water evaporates from the oceans and
cools to form clouds. The clouds move inland where they rise, condense and
fall as rain. This water gathers as lakes and streams and flows back to the
ocean in a continuous cycle. In the 7th century B.C., Thales of Miletus
believed that surface spray of the oceans was picked up by the wind and
carried inland to fall as rain. In earlier times people did not know the source
of underground water. They thought the water of the oceans, under the effect
of winds, was thrust towards the interior of the continents. They also believed
that the water returned by a secret passage, or the Great
Abyss. This passage
is connected to the oceans and has been called the ‘Tartarus’, since
Plato’s time. Even Descartes, a great thinker of the
eighteenth century, subscribed to
this view. Till the nineteenth century, Aristotle’s theory was prevalent.
According to this theory, water was condensed in cool mountain caverns and
formed underground lakes that fed springs. Today, we know that the
rainwater that seeps into the cracks of the ground is responsible for this.
The water cycle is described by the Qur’aan in the following
verses:
![]() “Seest
thou not that Allah Sends down rain from The sky, and leads it Through
springs in the earth? Then He causes to grow, Therewith, produce of
various Colours.” [Al-Qur’aan 39:21]
“Seest
thou not that Allah Sends down rain from The sky, and leads it Through
springs in the earth? Then He causes to grow, Therewith, produce of
various Colours.” [Al-Qur’aan 39:21] ![]()
![]() “He sends down rain From the sky And with it gives life to The earth
after it is dead: Verily in that are Signs For those who are wise.” [Al-Qur’aan
30:24]
“He sends down rain From the sky And with it gives life to The earth
after it is dead: Verily in that are Signs For those who are wise.” [Al-Qur’aan
30:24] ![]()
![]() “And We send down water From the sky according to (Due) measure,
and We cause it To soak in the soil; And We certainly are able To drain
it off (with ease).” [Al-Qur’aan 23:18]
“And We send down water From the sky according to (Due) measure,
and We cause it To soak in the soil; And We certainly are able To drain
it off (with ease).” [Al-Qur’aan 23:18] ![]()
![]() No other text dating back 1400 years ago gives such an accurate description
of the water cycle.
No other text dating back 1400 years ago gives such an accurate description
of the water cycle. ![]()
![]() WINDS IMPREGNATE THE CLOUDS
WINDS IMPREGNATE THE CLOUDS ![]()
![]() “And We send the fecundating winds, Then cause the rain to descend
From the sky, therewith providing You with water (in abundance).” [Al-Qur’aan
15:22]
“And We send the fecundating winds, Then cause the rain to descend
From the sky, therewith providing You with water (in abundance).” [Al-Qur’aan
15:22] ![]()
![]() The Arabic word used here is lawâqih, which is the plural of
laqih from
laqaha, which means to impregnate or fecundate. In this context, impregnate
means that the wind pushes the clouds together increasing the condensation
that causes lightning and thus rain. A similar description is found in the
Qur’aan:
The Arabic word used here is lawâqih, which is the plural of
laqih from
laqaha, which means to impregnate or fecundate. In this context, impregnate
means that the wind pushes the clouds together increasing the condensation
that causes lightning and thus rain. A similar description is found in the
Qur’aan:
![]() “It is Allah Who sends The Winds, and they raise The Clouds:
then does He Spread them in the sky As He wills, and break them Into
fragments, until thou seest Raindrops issue from the midst Thereof: then
when He has Made them reach such Of His servants as He wills, Behold,
they do rejoice!” [Al-Qur’aan 30:48]
“It is Allah Who sends The Winds, and they raise The Clouds:
then does He Spread them in the sky As He wills, and break them Into
fragments, until thou seest Raindrops issue from the midst Thereof: then
when He has Made them reach such Of His servants as He wills, Behold,
they do rejoice!” [Al-Qur’aan 30:48] ![]()
![]() The Qur’aanic descriptions are absolutely accurate and agree perfectly with
modern data on hydrology. The water cycle is described in several verses of
the Glorious Qur’aan, including 3:9, 7:57, 13:17, 25:48- 49, 36:34, 50:9-11,
56:68-70, 67:30 and 86:11.
The Qur’aanic descriptions are absolutely accurate and agree perfectly with
modern data on hydrology. The water cycle is described in several verses of
the Glorious Qur’aan, including 3:9, 7:57, 13:17, 25:48- 49, 36:34, 50:9-11,
56:68-70, 67:30 and 86:11. ![]()
![]()
![]() -----------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------![]()
![]()
![]() MOUNTAINS ARE LIKE PEGS (STAKES)
MOUNTAINS ARE LIKE PEGS (STAKES) ![]()

![]() In Geology, the phenomenon of ‘folding’ is a recently discovered fact.
Folding is responsible for the formation of mountain ranges. The earth’s
crust, on which we live, is like a solid shell, while the
deeper layers are hot
and fluid, and thus inhospitable to any form of life. It is also known that the
stability of the mountains is linked to the phenomenon of folding, for it was
the folds that were to provide foundations for the relief that
constitute the mountains. Geologists tell us that the
radius of the Earth is about 3,750 miles
and the crust on which we live is very thin, ranging between 1 to 30 miles.
Since the crust is thin, it has a high possibility of shaking.
Mountains act like
stakes or tent pegs that hold the earth’s crust and give it stability. The Qur’aan
contains exactly such a description in the following verse:
In Geology, the phenomenon of ‘folding’ is a recently discovered fact.
Folding is responsible for the formation of mountain ranges. The earth’s
crust, on which we live, is like a solid shell, while the
deeper layers are hot
and fluid, and thus inhospitable to any form of life. It is also known that the
stability of the mountains is linked to the phenomenon of folding, for it was
the folds that were to provide foundations for the relief that
constitute the mountains. Geologists tell us that the
radius of the Earth is about 3,750 miles
and the crust on which we live is very thin, ranging between 1 to 30 miles.
Since the crust is thin, it has a high possibility of shaking.
Mountains act like
stakes or tent pegs that hold the earth’s crust and give it stability. The Qur’aan
contains exactly such a description in the following verse:
![]() “Have We not
made The earth as a wide Expanse, And the mountains as pegs?” [Al-Qur’aan
78:6-7]
“Have We not
made The earth as a wide Expanse, And the mountains as pegs?” [Al-Qur’aan
78:6-7] ![]()
![]() The word awtad means stakes or pegs (like those used to anchor a tent); they
are the deep foundations of geological folds. A book named ‘Earth’ is
considered as a basic reference textbook on geology in many universities
around the world. One of the authors of this book is Frank
Press, who was the
President of the Academy of Sciences in the USA for 12 years and was the
Science Advisor to former US President Jimmy Carter. In this book he
illustrates the mountain in a wedge-shape and the mountain itself as a
small
part of the whole, whose root is deeply entrenched in the
ground. According
to Dr. Press, the mountains play an important role in stabilizing the crust of
the earth.
The word awtad means stakes or pegs (like those used to anchor a tent); they
are the deep foundations of geological folds. A book named ‘Earth’ is
considered as a basic reference textbook on geology in many universities
around the world. One of the authors of this book is Frank
Press, who was the
President of the Academy of Sciences in the USA for 12 years and was the
Science Advisor to former US President Jimmy Carter. In this book he
illustrates the mountain in a wedge-shape and the mountain itself as a
small
part of the whole, whose root is deeply entrenched in the
ground. According
to Dr. Press, the mountains play an important role in stabilizing the crust of
the earth. ![]()
(* Earth, Press and Siever, p. 435. Also see Earth Science, Tarbuck and Lutgens, p. 157.)
![]() The Qur’aan clearly mentions the function of the mountains in preventing the
earth from shaking:
The Qur’aan clearly mentions the function of the mountains in preventing the
earth from shaking:
![]() “And We have set on the earth Mountains standing
firm, Lest it should shake with them.” [Al-Qur’aan 21:31]
“And We have set on the earth Mountains standing
firm, Lest it should shake with them.” [Al-Qur’aan 21:31]
![]()
![]() The Qur’aanic descriptions are in perfect agreement with modern geological
data.
The Qur’aanic descriptions are in perfect agreement with modern geological
data. ![]()
![]() MOUNTAINS FIRMLY FIXED
MOUNTAINS FIRMLY FIXED ![]()
![]() The surface of the earth is broken into many rigid plates that are about
100
km in thickness. These plates float on a partially molten region called
aesthenosphere. Mountain formations occur at the boundary of the
plates. The
earth’s crust is 5 km thick below oceans, about 35 km thick below flat
continental surfaces and almost 80 km thick below great mountain ranges.
These are the strong foundations on which mountains stand. The Qur’aan also
speaks about the strong mountain foundations in the following verse:
The surface of the earth is broken into many rigid plates that are about
100
km in thickness. These plates float on a partially molten region called
aesthenosphere. Mountain formations occur at the boundary of the
plates. The
earth’s crust is 5 km thick below oceans, about 35 km thick below flat
continental surfaces and almost 80 km thick below great mountain ranges.
These are the strong foundations on which mountains stand. The Qur’aan also
speaks about the strong mountain foundations in the following verse:
![]() “And
the mountains Hath He firmly fixed.” [Al-Qur’aan 79:32]
“And
the mountains Hath He firmly fixed.” [Al-Qur’aan 79:32]
![]()
(*A similar message is contained in the Qur'aan in 88:19, 31:10 and 16:15)
![]()
![]() -----------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------![]()
![]()
![]() BARRIER BETWEEN SWEET AND SALT WATERS
BARRIER BETWEEN SWEET AND SALT WATERS ![]()
![]() Consider the following Qur’aanic verses:
Consider the following Qur’aanic verses:

![]() “He has let free the two bodies Of
flowing water, Meeting together: Between them is a Barrier Which they
do not transgress.” [Al-Qur’aan 55:19-20]
“He has let free the two bodies Of
flowing water, Meeting together: Between them is a Barrier Which they
do not transgress.” [Al-Qur’aan 55:19-20] ![]()
![]() In the Arabic text the word barzakh means a barrier or a
partition. This barrier
is not a physical partition. The Arabic word maraja literally means ‘they both
meet and mix with each other’. Early commentators of the Qur’aan were
unable to explain the two opposite meanings for the two bodies of water, i.e.
they meet and mix, and at the same time, there is a barrier between
them.
Modern Science has discovered that in the places where two different
seas meet, there is a barrier between them. This barrier divides the two seas so that
each sea has its own temperature, salinity and density. Oceanologists are
now in a better position to explain this verse. There is a slanted unseen water
barrier between the two seas through which water from one sea passes to the
other.
In the Arabic text the word barzakh means a barrier or a
partition. This barrier
is not a physical partition. The Arabic word maraja literally means ‘they both
meet and mix with each other’. Early commentators of the Qur’aan were
unable to explain the two opposite meanings for the two bodies of water, i.e.
they meet and mix, and at the same time, there is a barrier between
them.
Modern Science has discovered that in the places where two different
seas meet, there is a barrier between them. This barrier divides the two seas so that
each sea has its own temperature, salinity and density. Oceanologists are
now in a better position to explain this verse. There is a slanted unseen water
barrier between the two seas through which water from one sea passes to the
other. ![]()
(Principles of Oceanography, Davis, pp. 92-93.)
![]() But when the water from one sea enters the other sea, it loses its distinctive
characteristic and becomes homogenized with the other water. In a way this
barrier serves as a transitional homogenizing area for the two waters. This
scientific phenomenon mentioned in the Qur’aan was also confirmed by
Dr.
William Hay who is a well-known marine scientist and Professor of
Geological Sciences at the University of Colorado, U.S.A. The Qur’aan
mentions this phenomenon also in the following verse:
But when the water from one sea enters the other sea, it loses its distinctive
characteristic and becomes homogenized with the other water. In a way this
barrier serves as a transitional homogenizing area for the two waters. This
scientific phenomenon mentioned in the Qur’aan was also confirmed by
Dr.
William Hay who is a well-known marine scientist and Professor of
Geological Sciences at the University of Colorado, U.S.A. The Qur’aan
mentions this phenomenon also in the following verse:
![]() “And made a
separating bar between the two bodies Of flowing water?” [Al-Qur’aan
27:61]
“And made a
separating bar between the two bodies Of flowing water?” [Al-Qur’aan
27:61] ![]()
![]() This phenomenon occurs in several places, including the divider between the
Mediterranean and the Atlantic Ocean at Gibralter. But when the Qur’aan
speaks about the divider between fresh and salt water, it mentions the
existence of “a forbidding partition” with the barrier.
This phenomenon occurs in several places, including the divider between the
Mediterranean and the Atlantic Ocean at Gibralter. But when the Qur’aan
speaks about the divider between fresh and salt water, it mentions the
existence of “a forbidding partition” with the barrier.
![]() “It is He Who has Let
free the two bodies Of flowing water: One palatable and sweet, And the
other salty and bitter; Yet has He Made a barrier between them, And a
partition that is forbidden To be passed.” [Al-Qur’aan 25:53]
“It is He Who has Let
free the two bodies Of flowing water: One palatable and sweet, And the
other salty and bitter; Yet has He Made a barrier between them, And a
partition that is forbidden To be passed.” [Al-Qur’aan 25:53]
![]()
![]() Modern science has discovered that in estuaries, where fresh (sweet) and salt-water
meet, the situation is somewhat different from that found in places
where two seas meet. It has been discovered that what distinguishes
fresh
water from salt water in estuaries is a “pycnocline zone with a marked density
discontinuity separating the two layers.” This partition (zone of separation)
has salinity different from both the fresh water and the salt water.
Modern science has discovered that in estuaries, where fresh (sweet) and salt-water
meet, the situation is somewhat different from that found in places
where two seas meet. It has been discovered that what distinguishes
fresh
water from salt water in estuaries is a “pycnocline zone with a marked density
discontinuity separating the two layers.” This partition (zone of separation)
has salinity different from both the fresh water and the salt water.
![]()
![]() This phenomenon occurs in several places, including Egypt, where the river
Nile flows into the Mediterranean Sea.
This phenomenon occurs in several places, including Egypt, where the river
Nile flows into the Mediterranean Sea. ![]()
(Oceanography, Gross, p. 242. Also see Introductory Oceanography, Thurman,
pp. 300-301.)
(Oceanography, Gross, p. 244 and Introductory Oceanography, Thurman, pp.
300-301. )
![]() DARKNESS IN THE DEPTHS OF THE OCEAN
DARKNESS IN THE DEPTHS OF THE OCEAN ![]()
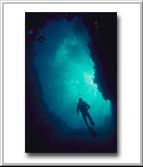
![]() Prof. Durga Rao is an expert in the field of Marine Geology and was a
professor at King Abdul Aziz University in Jeddah. He was asked to
comment on the following verse:
Prof. Durga Rao is an expert in the field of Marine Geology and was a
professor at King Abdul Aziz University in Jeddah. He was asked to
comment on the following verse:
![]() “Or (the Unbelievers’ state) Is like the
depths of darkness In a vast deep ocean, Overwhelmed with billow
Topped by billow, Topped by (dark) clouds: Depths of darkness, one
Above another: if a man Stretches out his hand, He can hardly see it! For
any to whom Allah Giveth not light, there is no light!” [Al-Qur’aan 24:40]
“Or (the Unbelievers’ state) Is like the
depths of darkness In a vast deep ocean, Overwhelmed with billow
Topped by billow, Topped by (dark) clouds: Depths of darkness, one
Above another: if a man Stretches out his hand, He can hardly see it! For
any to whom Allah Giveth not light, there is no light!” [Al-Qur’aan 24:40]
![]()
![]() Prof. Rao said that scientists have only now been able to confirm, with the
help of modern equipment that there is darkness in the depths of the
ocean.
Humans are unable to dive unaided underwater for more than 20 to 30 meters,
and cannot survive in the deep oceanic regions at a depth of more than 200
meters. This verse does not refer to all seas because not every sea can be
described as having accumulated darkness layered one over another. It refers
especially to a deep sea or deep ocean, as the Qur’aan says, “darkness in a
vast deep ocean”. This layered darkness in a deep ocean is the
result of two
causes:
Prof. Rao said that scientists have only now been able to confirm, with the
help of modern equipment that there is darkness in the depths of the
ocean.
Humans are unable to dive unaided underwater for more than 20 to 30 meters,
and cannot survive in the deep oceanic regions at a depth of more than 200
meters. This verse does not refer to all seas because not every sea can be
described as having accumulated darkness layered one over another. It refers
especially to a deep sea or deep ocean, as the Qur’aan says, “darkness in a
vast deep ocean”. This layered darkness in a deep ocean is the
result of two
causes: ![]()
-
 A light ray is composed of seven colours. These seven colours are Violet,
Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red (VIBGYOR). The light ray
undergoes refraction when it hits water. The upper 10 to 15 metres of
water absorb the red colour. Therefore if a diver is 25 metres under water and
gets wounded, he would not be able to see the red colour of his blood,
because the red colour does not reach this depth. Similarly orange rays are
absorbed at 30 to 50 metres, yellow at 50 to 100 metres, green at 100 to 200
metres, and finally, blue beyond 200 metres and violet and indigo above 200
metres. Due to successive disappearance of colour, one layer after another,
the ocean progressively becomes darker, i.e. darkness takes place in layers of
light. Below a depth of 1000 meters there is complete darkness.
A light ray is composed of seven colours. These seven colours are Violet,
Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red (VIBGYOR). The light ray
undergoes refraction when it hits water. The upper 10 to 15 metres of
water absorb the red colour. Therefore if a diver is 25 metres under water and
gets wounded, he would not be able to see the red colour of his blood,
because the red colour does not reach this depth. Similarly orange rays are
absorbed at 30 to 50 metres, yellow at 50 to 100 metres, green at 100 to 200
metres, and finally, blue beyond 200 metres and violet and indigo above 200
metres. Due to successive disappearance of colour, one layer after another,
the ocean progressively becomes darker, i.e. darkness takes place in layers of
light. Below a depth of 1000 meters there is complete darkness.

(Oceans, Elder and Pernetta, p. 27. 1 2)
-
 The sun’s rays are absorbed by clouds, which in turn scatter light rays
thus causing a layer of darkness under the clouds. This is the first layer
of darkness. When light rays reach the surface of the ocean they are
reflected by the wave surface giving it a shiny appearance. Therefore it is the
waves which reflect light and cause darkness. The un-reflected light penetrates
into the depths of the ocean. Therefore the ocean has two parts.
The surface
characterized by light and warmth and the depth characterized by darkness.
The surface is further separated from the deep part of the ocean by waves.
The internal waves cover the deep waters of seas and oceans because the deep
waters have a higher density than the waters above them. The darkness begins
below the internal waves. Even the fish in the depths of the ocean cannot see;
their only source of light is from their own bodies.
The sun’s rays are absorbed by clouds, which in turn scatter light rays
thus causing a layer of darkness under the clouds. This is the first layer
of darkness. When light rays reach the surface of the ocean they are
reflected by the wave surface giving it a shiny appearance. Therefore it is the
waves which reflect light and cause darkness. The un-reflected light penetrates
into the depths of the ocean. Therefore the ocean has two parts.
The surface
characterized by light and warmth and the depth characterized by darkness.
The surface is further separated from the deep part of the ocean by waves.
The internal waves cover the deep waters of seas and oceans because the deep
waters have a higher density than the waters above them. The darkness begins
below the internal waves. Even the fish in the depths of the ocean cannot see;
their only source of light is from their own bodies. 
![]() The Qur’aan rightly mentions: “Darkness in a vast deep ocean
overwhelmed with waves topped by waves”.
In other words, above these waves there are more types of waves, i.e. those
found on the surface of the ocean. The Qur’aanic verse continues, “topped by
(dark) clouds; depths of darkness, one above another.”
The Qur’aan rightly mentions: “Darkness in a vast deep ocean
overwhelmed with waves topped by waves”.
In other words, above these waves there are more types of waves, i.e. those
found on the surface of the ocean. The Qur’aanic verse continues, “topped by
(dark) clouds; depths of darkness, one above another.” ![]()
![]() These clouds as explained are barriers one over the other that further cause
darkness by absorption of colours at different levels.
These clouds as explained are barriers one over the other that further cause
darkness by absorption of colours at different levels. ![]()
![]() Prof. Durga Rao concluded by saying, “1400 years ago a normal human being
could not explain this phenomenon in so much detail. Thus the information
must have come from a supernatural
source”.
Prof. Durga Rao concluded by saying, “1400 years ago a normal human being
could not explain this phenomenon in so much detail. Thus the information
must have come from a supernatural
source”.![]()
![]()
![]() -----------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------![]()
![]()



